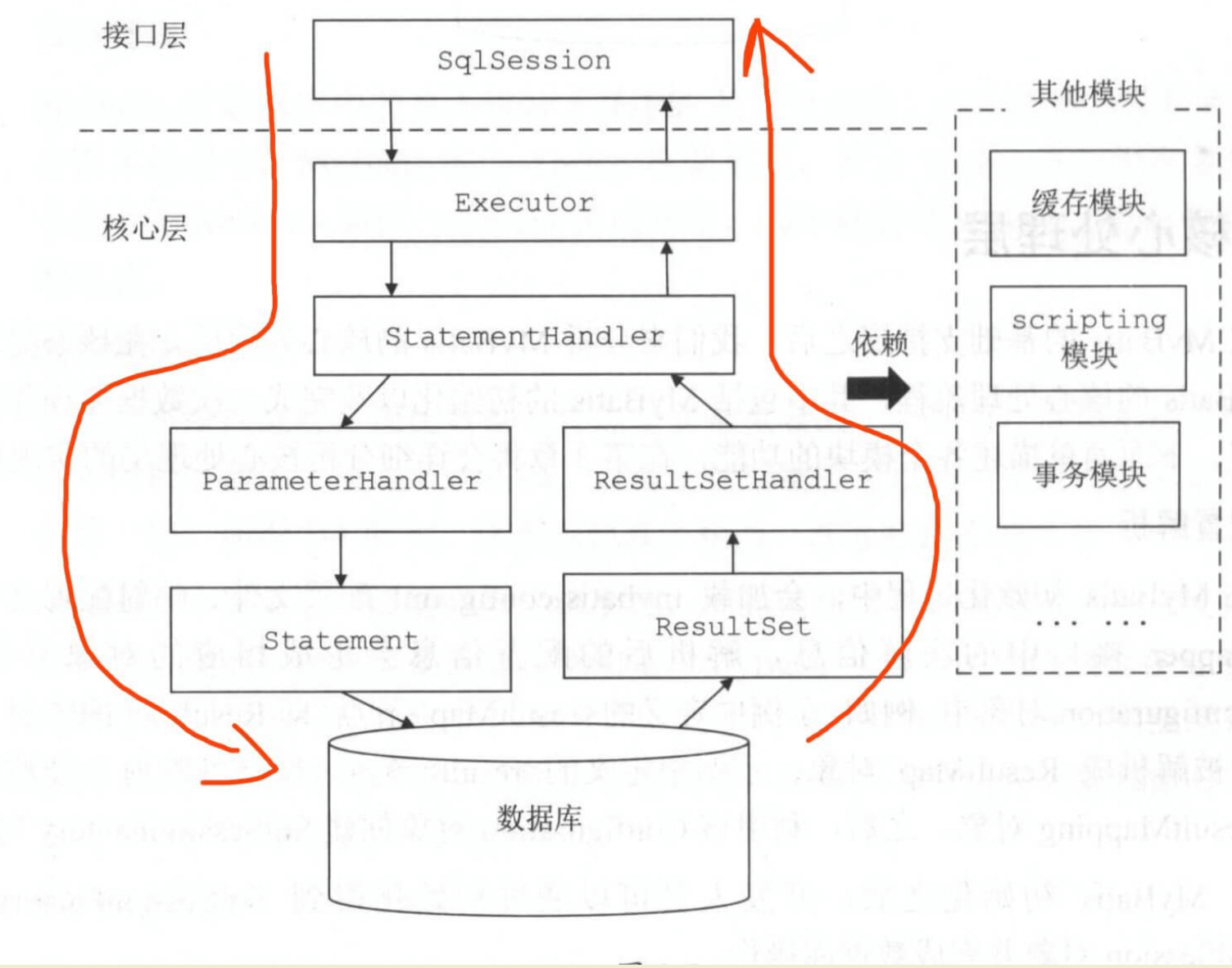
Executor
Executor
- 基本功能:改、查,没有增删的原因是,所有的增删操作都可以归结到改,它会将数据库相关操作委托给 StatementHandler完成。
- 缓存维护:一级缓存和二级缓存,功能包括创建缓存Key、清理缓存、判断缓存是否存在。
- 事物管理:提交、回滚、关闭、批处理刷新。
Executor 的创建时机和创建策略
Executor 的创建时机是,创建 DefaultSqlSession 实例时,作为构造参数传递进去。(见 DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java 内)
# DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java
Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
# DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
// 获得执行器类型
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; // 使用默认
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; // 使用 ExecutorType.SIMPLE
// 创建对应实现的 Executor 对象
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 如果开启缓存,创建 CachingExecutor 对象,进行包装
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 应用插件
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
Executor 有三种创建策略。
public enum ExecutorType {
SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH
}
有两种手段来指定 Executor 创建策略。
第一种,configuration 配置文件中,配置默认 ExecutorType 类型。(当不配置时,默认为 ExecutorType.SIMPLE)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="REUSE" />
</settings>
</configuration>
第二种,手动给 DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java 的创建 SqlSession 的方法传递 ExecutorType 参数。
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, autoCommit);
}
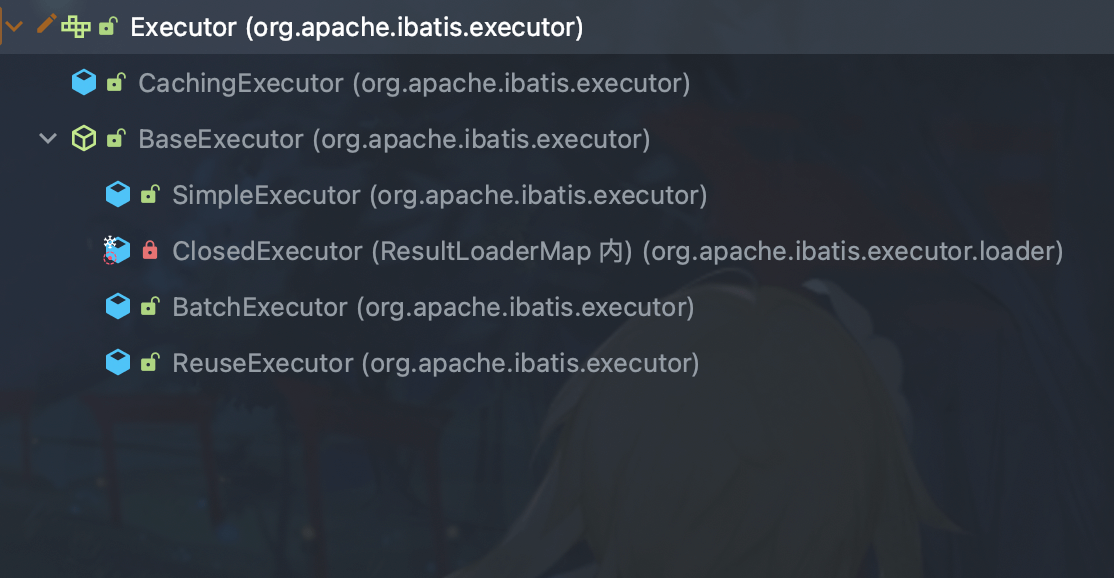
- Executor 的直接子类有 BaseExecutor 和 CachingExecutor 。
- CachingExecutor 在 BaseExecutor 的基础上,实现二级缓存功能。
- BaseExecutor 的本地缓存,就是一级缓存。
/**
* 执行器接口
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface Executor {
// 空 ResultHandler 对象的枚举
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
// 更新 or 插入 or 删除,由传入的 MappedStatement 的 SQL 所决定
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
// 查询,带 ResultHandler + CacheKey + BoundSql
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
// 查询,带 ResultHandler
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
// 查询,返回值为 Cursor
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
// 刷入批处理语句
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
// 提交事务
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
// 回滚事务
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
// 创建 CacheKey 对象
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
// 判断是否缓存
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
// 清除本地缓存
void clearLocalCache();
// 延迟加载
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
// 获得事务
Transaction getTransaction();
// 关闭事务
void close(boolean forceRollback);
// 判断事务是否关闭
boolean isClosed();
// 设置包装的 Executor 对象
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
BaseExecutor
提供骨架方法,子类只要实现指定的几个抽象方法(经典的模板设计模式),BaseExecutor 主要是用于维护一级缓存和事务。
事务是通过会话中调用commit、rollback进行管理。它实现了Executor中的Query与update方法。会话中SQL请求,正是调用的这两个方法。Query方法中处理一级缓存逻辑,即根据SQL及参数判断缓存中是否存在数据,有就走缓存。否则就会调用子类的doQuery() 方法去查询数据库,然后在设置缓存。在doUpdate() 中主要是用于清空缓存。
/**
* 修改操作
*/
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
// 已经关闭 则抛出 ExecutorException 异常
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
// 执行写操作
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
/**
* 清空本地缓存
*/
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
// 清理 localCache
localCache.clear();
// 清理 localOutputParameterCache
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
/**
* 查询操作
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获得 BoundSql 对象
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 创建 CacheKey 对象
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
/**
* 查询操作
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
// 已经关闭,则抛出 ExecutorException 异常
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清空本地缓存,如果 queryStack 为零,并且要求清空本地缓存。
// flushCacheRequired设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空,默认值:false。
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
// queryStack + 1
queryStack++;
// 从一级缓存中,获取查询结果 (前提是你不能自定义返回处理)
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
// 获取到,则进行处理
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
// 获得不到,则从数据库中查询
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
// queryStack - 1
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
// 执行延迟加载
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
// 清空 deferredLoads
deferredLoads.clear();
// 如果缓存级别是 LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT ,则进行清理
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* 创建缓存key 可以看到只有 statementId、分页参数、sql、查询参数、环境id 这六个参数相同 我们才认为key相同 才会查询到缓存
*/
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 创建 CacheKey 对象
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
// 设置 id、offset、limit、sql 到 CacheKey 对象中
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
// 设置 ParameterMapping 数组的元素对应的每个 value 到 CacheKey 对象中
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic 这块逻辑,和 DefaultParameterHandler 获取 value 是一致的。
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
// 设置 Environment.id 到 CacheKey 对象中
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
/**
* 提交
*/
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
// 已经关闭,则抛出 ExecutorException 异常
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
// 清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
// 刷入批处理语句
flushStatements();
// 是否要求提交事务。如果是,则提交事务。
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
}
/**
* 回滚
*/
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (!closed) {
try {
// 清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
// 刷入批处理语句
flushStatements(true);
} finally {
if (required) {
// 是否要求回滚事务。如果是,则回滚事务。
transaction.rollback();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 从数据库中读取操作
*/
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 在缓存中,添加占位对象。此处的占位符,和延迟加载有关,可见 `DeferredLoad#canLoad()` 方法
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 执行读操作
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 从缓存中,移除占位对象
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 添加到缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
// 暂时忽略,存储过程相关
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
SimpleExecutor
SimpleExecutor是默认执行器,它的行为是每处理一次会话当中的SQl请求都会通过对应的StatementHandler 构建一个新个Statement。
/**
* 简单的 Executor 实现类。
* <p>
* 1. 每次开始读或写操作,都创建对应的 Statement 对象。
* 2. 执行完成后,关闭该 Statement 对象。
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
// 初始化 StatementHandler 对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行写操作
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
// 关闭 StatementHandler 对象
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 初始化 StatementHandler 对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行读操作
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
// 关闭 StatementHandler 对象
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
// 初始化 StatementHandler 对象
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 设置 Statement ,如果执行完成,则进行自动关闭
stmt.closeOnCompletion();
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行读操作
return handler.queryCursor(stmt);
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
// 不做批量处理 直接返回空
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 初始化 StatementHandler 对象
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获得 Connection 对象
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 创建 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
}
ReuseExecutor
ReuseExecutor 区别在于他会将在会话期间内的Statement进行缓存,并使用SQL语句作为Key。所以当执行下一请求的时候,不在重复构建Statement,而是从缓存中取出并设置参数,然后执行。
依赖 Map<String, Statement> 来完成对 Statement 的重用的(用完不关)。什么时候关闭这些 Statement 对象的?方法 flushStatements()用来处理这些 Statement 对象。
在执行 commit、rollback 等动作前,将会执行 flushStatements () 方法,将 Statement 对象逐一关闭。可参看 BaseExecutor 源码。
public class ReuseExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
// key=sql, value=Statement,不同的sql,对应不同的Statement
private final Map<String, Statement> statementMap = new HashMap<String, Statement>();
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
// 初始化 StatementHandler 对象
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行写操作
return handler.update(stmt);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 初始化 StatementHandler 对象
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行读操作
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// sql是key,不同的sql,将产生不同的Statement
if (hasStatementFor(sql)) {
// 从statementMap中获取Statement
stmt = getStatement(sql);
} else {
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
// 将Statement放到statementMap中
putStatement(sql, stmt);
}
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// ...
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
// 关闭缓存的 Statement 对象们
for (Statement stmt : statementMap.values()) {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
statementMap.clear();
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
BatchExecutor
执行 update(没有 select,JDBC 批处理不支持 select),将所有 sql 都添加到批处理中(addBatch ()),等待统一执行(executeBatch ()),它缓存了多个 Statement 对象,每个 Statement 对象都是 addBatch () 完毕后,等待逐一执行 executeBatch () 批处理的;BatchExecutor 相当于维护了多个桶,每个桶里都装了很多属于自己的 SQL,就像苹果蓝里装了很多苹果,番茄蓝里装了很多番茄,最后,再统一倒进仓库。(可以是 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象)
/**
* 批量执行的 Executor 实现类
*
* @author Jeff Butler
*/
public class BatchExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public static final int BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE = Integer.MIN_VALUE + 1002;
/**
* Statement 数组
*/
private final List<Statement> statementList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* BatchResult 数组
* <p>
* 每一个 BatchResult 元素,对应一个 {@link #statementList} 的 Statement 元素
*/
private final List<BatchResult> batchResultList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 当前 SQL
*/
private String currentSql;
/**
* 当前 MappedStatement 对象
*/
private MappedStatement currentStatement;
public BatchExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
super(configuration, transaction);
}
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
final StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
final BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
final String sql = boundSql.getSql();
final Statement stmt;
// 如果匹配最后一次 currentSql 和 currentStatement ,则聚合到 BatchResult 中
if (sql.equals(currentSql) && ms.equals(currentStatement)) {
// 获得最后一次的 Statement 对象
int last = statementList.size() - 1;
stmt = statementList.get(last);
// 设置事务超时时间
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
// 设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt);//fix Issues 322
// 获得最后一次的 BatchResult 对象,并添加参数到其中
BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(last);
batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject);
// 如果不匹配最后一次 currentSql 和 currentStatement ,则新建 BatchResult 对象
} else {
// 获得 Connection
Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
// 创建 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt); //fix Issues 322
// 重新设置 currentSql 和 currentStatement
currentSql = sql;
currentStatement = ms;
// 添加 Statement 到 statementList 中
statementList.add(stmt);
// 创建 BatchResult 对象,并添加到 batchResultList 中
batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject));
}
// handler.parameterize(stmt);
// 批处理
handler.batch(stmt);
return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE;
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 刷入批处理语句
flushStatements();
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 获得 Connection 对象
Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
// 创建 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt);
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行读操作
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
// 关闭 StatementHandler 对象
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 刷入批处理语句
flushStatements();
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建 StatementHandler 对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
// 获得 Connection 对象
Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
// 创建 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象
Statement stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置 Statement ,如果执行完成,则进行自动关闭
stmt.closeOnCompletion();
// 设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt);
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行读操作
return handler.queryCursor(stmt);
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
try {
// 如果 isRollback 为 true ,返回空数组
if (isRollback) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 遍历 statementList 和 batchResultList 数组,逐个提交批处理
List<BatchResult> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0, n = statementList.size(); i < n; i++) {
// 获得 Statement 和 BatchResult 对象
Statement stmt = statementList.get(i);
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(i);
try {
// 批量执行
batchResult.setUpdateCounts(stmt.executeBatch());
//
MappedStatement ms = batchResult.getMappedStatement();
List<Object> parameterObjects = batchResult.getParameterObjects();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = ms.getKeyGenerator();
if (Jdbc3KeyGenerator.class.equals(keyGenerator.getClass())) {
Jdbc3KeyGenerator jdbc3KeyGenerator = (Jdbc3KeyGenerator) keyGenerator;
jdbc3KeyGenerator.processBatch(ms, stmt, parameterObjects);
} else if (!NoKeyGenerator.class.equals(keyGenerator.getClass())) { //issue #141
for (Object parameter : parameterObjects) {
keyGenerator.processAfter(this, ms, stmt, parameter);
}
}
// Close statement to close cursor #1109
// 关闭 Statement 对象
closeStatement(stmt);
} catch (BatchUpdateException e) {
// 如果发生异常,则抛出 BatchExecutorException 异常
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
message.append(batchResult.getMappedStatement().getId())
.append(" (batch index #")
.append(i + 1)
.append(")")
.append(" failed.");
if (i > 0) {
message.append(" ")
.append(i)
.append(" prior sub executor(s) completed successfully, but will be rolled back.");
}
throw new BatchExecutorException(message.toString(), e, results, batchResult);
}
// 添加到结果集
results.add(batchResult);
}
return results;
} finally {
// 关闭 Statement 们
for (Statement stmt : statementList) {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
// 置空 currentSql、statementList、batchResultList 属性
currentSql = null;
statementList.clear();
batchResultList.clear();
}
}
}
CachingExecutor
装饰设计模式典范,先从缓存中获取查询结果,存在就返回,不存在,再委托给 Executor delegate 去数据库取,delegate 可以是上面任一的 SimpleExecutor、ReuseExecutor、BatchExecutor。
/**
* 支持二级缓存的 Executor 的实现类
*
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
/**
* 被委托的 Executor 对象
*/
private final Executor delegate;
/**
* TransactionalCacheManager 对象
*/
private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
// 设置 delegate 被当前执行器所包装
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
return delegate.getTransaction();
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
//issues #499, #524 and #573
// 如果强制回滚,则回滚 TransactionalCacheManager
if (forceRollback) {
tcm.rollback();
// 如果强制提交,则提交 TransactionalCacheManager
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {
return delegate.isClosed();
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
// 如果需要清空缓存,则进行清空
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获得 BoundSql 对象
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 创建 CacheKey 对象
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 查询
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException {
// 如果需要清空缓存,则进行清空
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
return delegate.queryCursor(ms, parameter, rowBounds);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 如果需要清空缓存,则进行清空
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
// 暂时忽略,存储过程相关
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 从二级缓存中,获取结果
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
// 如果不存在,则从数据库中查询
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 缓存结果到二级缓存中
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
// 如果存在,则直接返回结果
return list;
}
}
// 不使用缓存,则从数据库中查询
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
return delegate.flushStatements();
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
delegate.commit(required);
// 提交 TransactionalCacheManager
tcm.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
// 回滚 TransactionalCacheManager
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
private void ensureNoOutParams(MappedStatement ms, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.IN) {
throw new ExecutorException("Caching stored procedures with OUT params is not supported. Please configure useCache=false in " + ms.getId() + " statement.");
}
}
}
}
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
return delegate.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
@Override
public boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key) {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
return delegate.isCached(ms, key);
}
@Override
public void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType) {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
delegate.deferLoad(ms, resultObject, property, key, targetType);
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
delegate.clearLocalCache();
}
/**
* 如果需要清空缓存,则进行清空
*
* @param ms MappedStatement 对象
*/
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { // 是否需要清空缓存
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
@Override
public void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This method should not be called");
}
}
一级缓存
每当我们使用 MyBatis 开启一次和数据库的会话,MyBatis 会创建出一个 SqlSession 对象表示一次数据库会话,而每个 SqlSession 都会创建一个 Executor 对象。
在对数据库的一次会话中,我们有可能会反复地执行完全相同的查询语句,如果不采取一些措施的话,每一次查询都会查询一次数据库,而我们在极短的时间内做了完全相同的查询,那么它们的结果极有可能完全相同,由于查询一次数据库的代价很大,这有可能造成很大的资源浪费。
为了解决这一问题,减少资源的浪费,MyBatis 会在表示会话的SqlSession 对象中建立一个简单的缓存,将每次查询到的结果结果缓存起来,当下次查询的时候,如果判断先前有个完全一样的查询,会直接从缓存中直接将结果取出,返回给用户,不需要再进行一次数据库查询了。 注意,这个“简单的缓存”就是一级缓存,且默认开启,无法关闭。
如下图所示,MyBatis 会在一次会话的表示 —— 一个 SqlSession 对象中创建一个本地缓存(
localCache),对于每一次查询,都会尝试根据查询的条件去本地缓存中查找是否在缓存中,如果在缓存中,就直接从缓存中取出,然后返回给用户;否则,从数据库读取数据,将查询结果存入缓存并返回给用户。
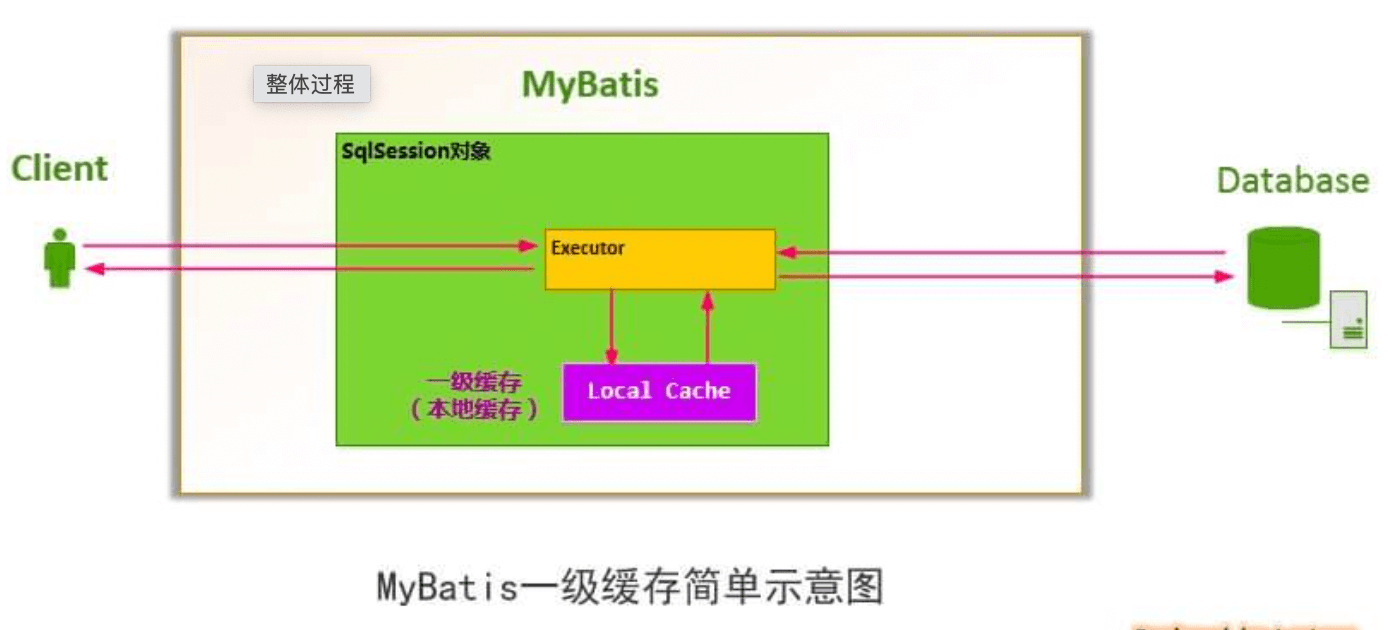
一级缓存的命中场景
关于一级缓存的命中可大致分为两个场景,满足特定命中参数,第二不触发清空方法。
- 缓存命中参数:
- SQL与参数相同:
- 同一个会话:
- 相同的MapperStatement ID:
- RowBounds行范围相同:
- 触发清空缓存
- 手动调用clearCache
- 执行提交回滚
- 执行update
- 配置flushCache=true
- 缓存作用域为Statement
一级缓存逻辑就存在于 BaseExecutor 里面。当会话接收到查询请求之后,会交给执行器的Query方法,在这里会通过 Sql、参数、分页条件等参数创建一个缓存key,在基于这个key去 PerpetualCache中查找对应的缓存值,如果有主直接返回。没有就会查询数据库,然后在填充缓存。
一级缓存的清空
缓存的清空对应BaseExecutor中的 clearLocalCache.方法。只要找到调用该方法地方,就知道哪些场景中会清空缓存了。
- update: 执行任意增删改
- select:查询又分为两种情况清空,1.前置清空,即配置了flushCache=true。2.后置清空,配置了缓存作用域为statement 查询结束合会清空缓存。
- commit:提交前清空
- Rolback:回滚前清空
注意:clearLocalCache 不是清空某条具体数据,而清当前会话下所有一级缓存数据
MyBatis集成Spring后一级缓存失效的问题?
原因是Spring 对SqlSession进行了封装,通过SqlSessionTemplae ,使得每次调用Sql,都会重新构建一个SqlSession,具体参见SqlSessionInterceptor。而根据前面所学,一级缓存必须是同一会话才能命中,所以在这些场景当中不能命中。
怎么解决呢?给Spring 添加事务即可。添加事物之后,SqlSessionInterceptor(会话拦截器)就会去判断两次请求是否在同一事务当中,如果是就会共用同一个SqlSession会话来解决。
/**
* 本地缓存 即一级缓存 基于HashMap实现
*/
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
二级缓存
上文中提到的一级缓存中,其最大的共享范围就是一个 SqlSession 内部,如果多个 SqlSession 之间需要共享缓存,则需要使用到二级缓存。开启二级缓存后,会使用 CachingExecutor 装饰 Executor ,进入一级缓存的查询流程前,先在 CachingExecutor 进行二级缓存的查询,具体的工作流程如下所示。
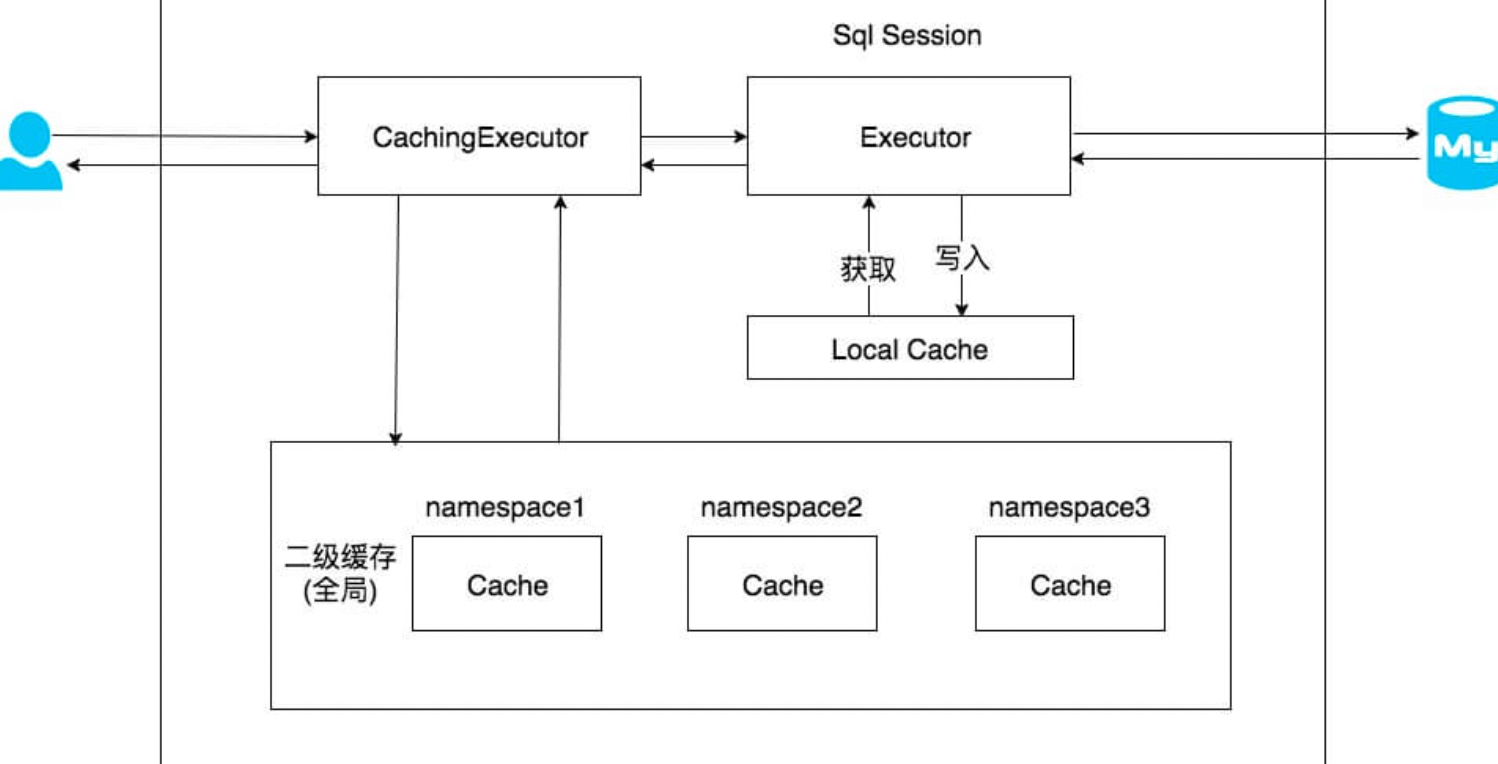
二缓存需求
二级缓存是一个完整的缓存解决方案,那应该包含哪些功能呢?这里我们分为核心功能和非核心功能两类:
- 存储【核心功能】
即缓存数据库存储在哪里?常用的方案如下:
- 内存:最简单就是在内存当中,不仅实现简单,而且速度快。内存弊端就是不能持久化,且容易有限。
- 硬盘:可以持久化,容量大。但访问速度不如内存,一般会结合内存一起使用。
- 第三方集成:在分布式情况,如果想和其它节点共享缓存,只能第三方软件进行集成。比如Redis.
- 溢出淘汰【核心功能】
无论哪种存储都必须有一个容易,当容量满的时候就要进行清除,清除的算法即溢出淘汰机制。常见算法如下:
- FIFO:先进先出
- LRU:最近最少使用
- WeakReference: 弱引用,将缓存对象进行弱引用包装,当Java进行gc的时候,不论当前的内存空间是否足够,这个对象都会被回收
- SoftReference:软件引用,基机与弱引用类似,不同在于只有当空间不足时GC才才回收软引用对象。
- 其它功能
- 过期清理:指清理存放数据过久的数据
- 线程安全:保证缓存可以被多个线程同时使用
- 写安全:当拿到缓存数据后,可对其进行修改,而不影响原本的缓存数据。通常采取做法是对缓存对象进行深拷贝。
二级缓存责任链设计
这么多的功能,如何才能简单的实现,并保证它的灵活性与扩展性呢?这里MyBatis抽像出Cache接口,其只定义了缓存中最基本的功能方法:
- 设置缓存
- 获取缓存
- 清除缓存
- 获取缓存数量
然后上述中每一个功能都会对应一个组件类,并基于装饰者加责任链的模式,将各个组件进行串联。在执行缓存的基本功能时,其它的缓存逻辑会沿着这个责任链依次往下传递。
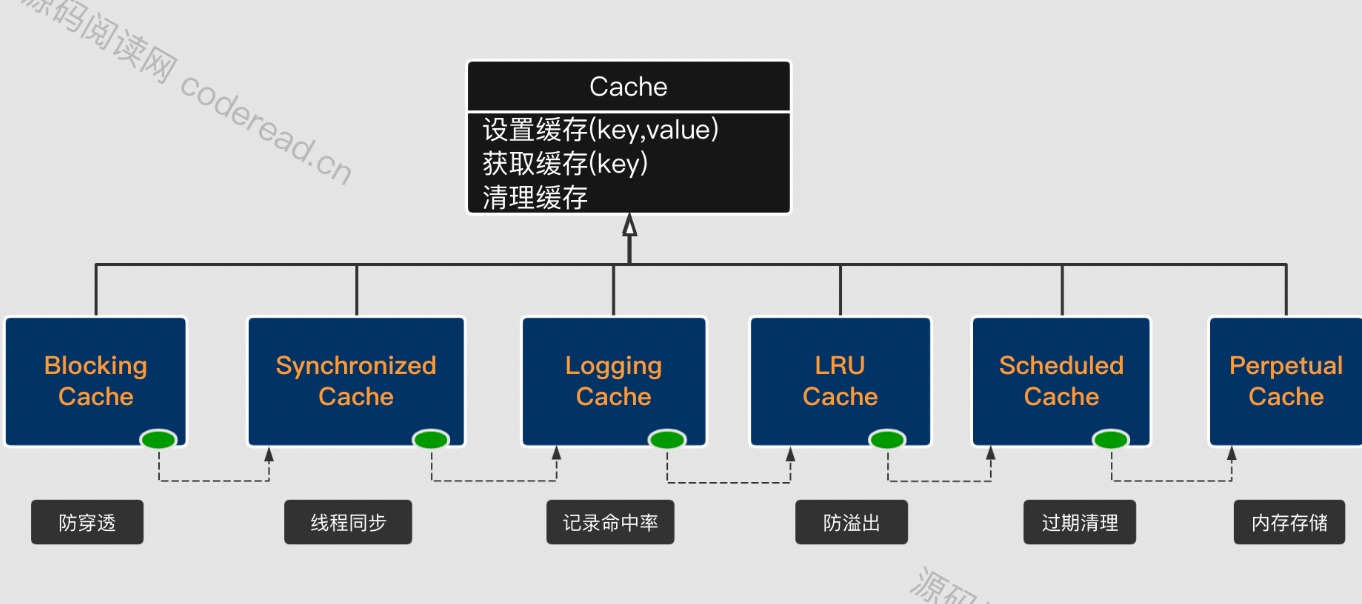
这样设计有以下优点:
- 职责单一:各个节点只负责自己的逻辑,不需要关心其它节点。
- 扩展性强:可根据需要扩展节点、删除节点,还可以调换顺序保证灵活性。
- 松耦合:各节点之间不没强制依赖其它节点。而是通过顶层的Cache接口进行间接依赖。
二级缓存的命中条件
二级缓存的命中场景与一级缓存类似,不同在于二级可以跨会放使用,还有就是二级缓存的更新,必须是在会话提交之后。
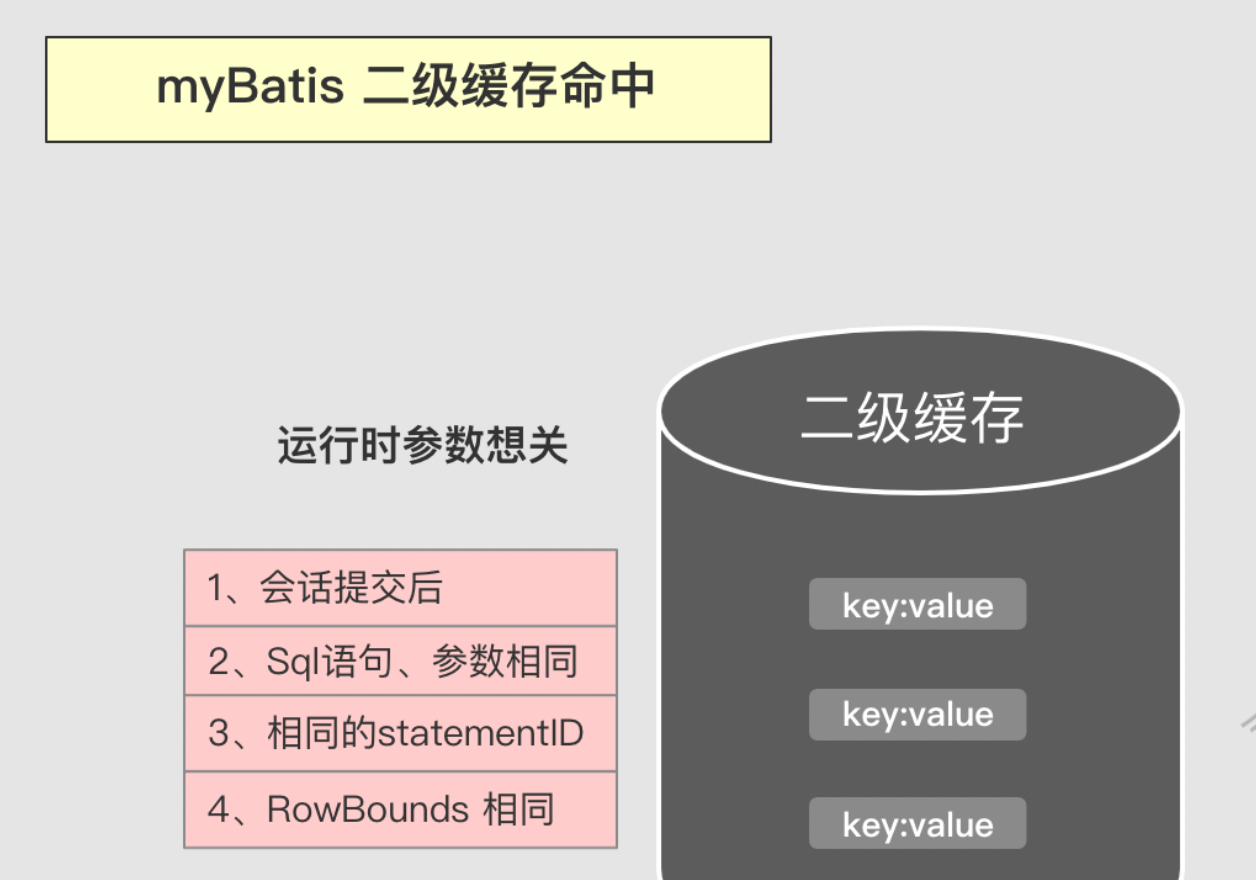
为什么要提交之后才能命中缓存?
防止脏读。
二级缓存结构
为了实现会话提交之后才变更二级缓存,MyBatis为每个会话设立了若干个暂存区,当前会话对指定缓存空间的变更,都存放在对应的暂存区,当会话提交之后才会提交到每个暂存区对应的缓存空间。为了统一管理这些暂存区,每个会话都一个唯一的事物缓存管理 器。
二级缓存执行流程
原本会话是通过Executor实现SQL调用,这里基于装饰器模式使用CachingExecutor对SQL调用逻辑进行拦截。以嵌入二级缓存相关逻辑。
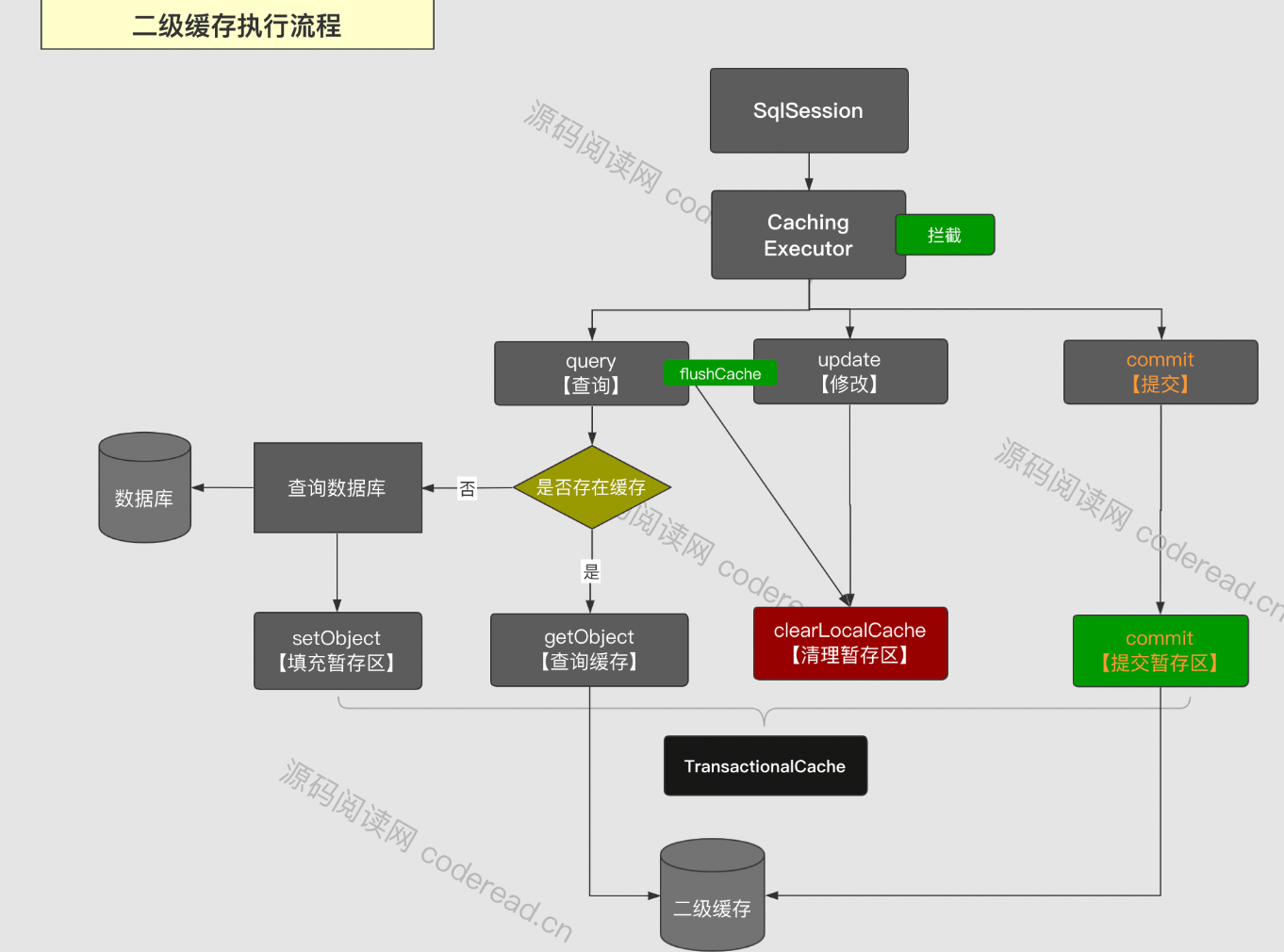
查询操作query
当会话调用query() 时,会基于查询语句、参数等数据组成缓存Key,然后尝试从二级缓存中读取数据。读到就直接返回,没有就调用被装饰的Executor去查询数据库,然后在填充至对应的暂存区。
请注意,这里的查询是实时从缓存空间读取的,而变更,只会记录在暂存区
更新操作update
当执行update操作时,同样会基于查询的语句和参数组成缓存KEY,然后在执行update之前清空缓存。这里清空只针对暂存区,同时记录清空的标记,以便当会话提交之时,依据该标记去清空二级缓存空间。
如果在查询操作中配置了flushCache=true ,也会执行相同的操作。
提交操作commit
当会话执行commit操作后,会将该会话下所有暂存区的变更,更新到对应二级缓存空间去。
TransactionalCacheManager
org.apache.ibatis.cache.TransactionalCacheManager ,TransactionalCache 管理器。
# TransactionalCacheManager.java
/**
* Cache 和 TransactionalCache 的映射
*/
private final Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap<>();
我们可以看到,
transactionalCaches是一个使用 Cache 作为 KEY ,TransactionalCache 作为 VALUE 的 Map 对象。为什么是一个 Map 对象呢?因为在一次的事务过程中,可能有多个不同的 MappedStatement 操作,而它们可能对应多个 Cache 对象。
TransactionalCache 是怎么创建的呢?答案在
#getTransactionalCache(Cache cache)方法,代码如下:# TransactionalCacheManager.java private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) { return transactionalCaches.computeIfAbsent(cache, TransactionalCache::new); }- 优先,从
transactionalCaches获得 Cache 对象,对应的 TransactionalCache 对象。 - 如果不存在,则创建一个 TransactionalCache 对象,并添加到
transactionalCaches中。
- 优先,从
putObject
#putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) 方法,添加 Cache + KV ,到缓存中。代码如下:
// TransactionalCacheManager.java
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
// 首先,获得 Cache 对应的 TransactionalCache 对象
// 然后,添加 KV 到 TransactionalCache 对象中
getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
getObject
#getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) 方法,获得缓存中,指定 Cache + K 的值。代码如下:
// TransactionalCacheManager.java
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
// 首先,获得 Cache 对应的 TransactionalCache 对象
// 然后从 TransactionalCache 对象中,获得 key 对应的值
return getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
clear
#clear() 方法,清空缓存。代码如下:
# TransactionalCacheManager.java
public void clear(Cache cache) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).clear();
}
commit
#commit() 方法,提交所有 TransactionalCache 。代码如下:
# TransactionalCacheManager.java
public void commit() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.commit();
}
}
- 通过调用该方法,TransactionalCache 存储的当前事务的缓存,会同步到其对应的 Cache 对象。
rollback
#rollback() 方法,回滚所有 TransactionalCache 。代码如下:
# TransactionalCacheManager.java
public void rollback() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.rollback();
}
}
TransactionalCache
org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.TransactionalCache ,实现 Cache 接口,支持事务的 Cache 实现类,主要用于二级缓存中。
# TransactionalCache.java
/**
* 委托的 Cache 对象。
*
* 实际上,就是二级缓存 Cache 对象。
*/
private final Cache delegate;
/**
* 提交时,清空 {@link #delegate}
*
* 初始时,该值为 false
* 清理后{@link #clear()} 时,该值为 true ,表示持续处于清空状态
*/
private boolean clearOnCommit;
/**
* 待提交的 KV 映射
*/
private final Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
/**
* 查找不到的 KEY 集合
*/
private final Set<Object> entriesMissedInCache;
public TransactionalCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.clearOnCommit = false;
this.entriesToAddOnCommit = new HashMap<>();
this.entriesMissedInCache = new HashSet<>();
}
- 在事务未提交时,
entriesToAddOnCommit属性,会暂存当前事务新产生的缓存 KV 对。 - 在事务提交时,
entriesToAddOnCommit属性,会同步到二级缓存delegate中。
getObject
# TransactionalCache.java
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// issue #116
// <1> 从 delegate 中获取 key 对应的 value
Object object = delegate.getObject(key);
// <2> 如果不存在,则添加到 entriesMissedInCache 中
if (object == null) {
entriesMissedInCache.add(key);
}
// issue #146
// <3> 如果 clearOnCommit 为 true ,表示处于持续清空状态,则返回 null
if (clearOnCommit) {
return null;
// <4> 返回 value
} else {
return object;
}
}
<1>处,调用delegate的#getObject(Object key)方法,从delegate中获取key对应的 value 。<2>处,如果不存在,则添加到entriesMissedInCache中。这是个神奇的逻辑???答案见commit()和#rollback()方法。<3>处,如果clearOnCommit为true,表示处于持续清空状态,则返回null。因为在事务未结束前,我们执行的清空缓存操作不好同步到delegate中,所以只好通过clearOnCommit来标记处于清空状态。那么,如果处于该状态,自然就不能返回delegate中查找的结果。<4>处,返回 value 。
putObject
#putObject(Object key, Object object) 方法,暂存 KV 到 entriesToAddOnCommit 中。代码如下:
# TransactionalCache.java
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
// 暂存 KV 到 entriesToAddOnCommit 中
entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
removeObject
# TransactionalCache.java
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return null;
}
clear
#clear() 方法,清空缓存。代码如下:
# TransactionalCache.java
@Override
public void clear() {
// <1> 标记 clearOnCommit 为 true
clearOnCommit = true;
// <2> 清空 entriesToAddOnCommit
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
}
<1>处,标记clearOnCommit为true。<2>处,清空entriesToAddOnCommit。- 该方法,不会清空
delegate的缓存。真正的清空,在事务提交时。
commit
#commit() 方法,提交事务。重头戏,代码如下:
# TransactionalCache.java
public void commit() {
// <1> 如果 clearOnCommit 为 true ,则清空 delegate 缓存
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
// 将 entriesToAddOnCommit、entriesMissedInCache 刷入 delegate 中
flushPendingEntries();
// 重置
reset();
}
<1>处,如果clearOnCommit为true,则清空delegate缓存。<2>处,调用#flushPendingEntries()方法,将entriesToAddOnCommit、entriesMissedInCache同步到delegate中。代码如下:// TransactionalCache.java private void flushPendingEntries() { // 将 entriesToAddOnCommit 刷入 delegate 中 for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet()) { delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } // 将 entriesMissedInCache 刷入 delegate 中 for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) { if (!entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) { delegate.putObject(entry, null); } } }- 在看这段代码时,笔者一直疑惑
entriesMissedInCache同步到delegate中,会不会存在问题。因为当前事务未查找到,不代表其他事务恰好实际能查到。这样,岂不是会将缓存错误的置空。后来一想,缓存即使真的被错误的置空,最多也就多从数据库中查询一次罢了。
- 在看这段代码时,笔者一直疑惑
<3>处,调用#reset()方法,重置对象。代码如下:// TransactionalCache.java private void reset() { // 重置 clearOnCommit 为 false clearOnCommit = false; // 清空 entriesToAddOnCommit、entriesMissedInCache entriesToAddOnCommit.clear(); entriesMissedInCache.clear(); }- 因为,一个 Executor 可以提交多次事务,而 TransactionalCache 需要被重用,那么就需要重置回初始状态。
rollback
#rollback() 方法,回滚事务。代码如下:
// TransactionalCache.java
public void rollback() {
// <1> 从 delegate 移除出 entriesMissedInCache
unlockMissedEntries();
// <2> 重置
reset();
}
<1>处,调用#unlockMissedEntries()方法,将entriesMissedInCache同步到delegate中。代码如下:// TransactionalCache.java private void unlockMissedEntries() { for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) { try { delegate.removeObject(entry); } catch (Exception e) { log.warn("Unexpected exception while notifiying a rollback to the cache adapter." + "Consider upgrading your cache adapter to the latest version. Cause: " + e); } } }- 即使事务回滚,也不妨碍在事务的执行过程中,发现
entriesMissedInCache不存在对应的缓存。
- 即使事务回滚,也不妨碍在事务的执行过程中,发现
<2>处,调用#reset()方法,重置对象。
